Colin James Physics - Mathematics data.

Last updated: 25th June 2013.
Greek alphabet.
Integrals - Algebraic functions.
Integrals - Hyperbolic functions.
Integrals - Trigonometrical functions.
Series and sequences.
Trigonometry.
Vector algebra (laws).
Trigonometry.
Contents of this page.

Trigonometric identities.
Compound angle formulae.
Double angle formulae.
The sine rule.
Trigonometric identities.
cos2q +
sin2q = 1
tanq =
sinq/cosq
provided cosq ¹ 0
cos(-q) =
cosq
sin(-q) =
-sinq
sin(p + q) =
-sinq
sin(p - q) =
sinq
sin(p/2 + q) =
cosq
sin(p/2 - q) =
cosq
cos(p + q) =
-cosq
cos(p - q) =
-cosq
cos(p/2 + q) =
-sinq
cos(p/2 - q) =
sinq
Compound angle formulae.
sin(a + b) =
sina cosb +
cosa sinb
sin(a - b) =
sina cosb -
cosa sinb
cos(a + b) =
cosa cosb -
sina sinb
cos(a - b) =
cosa cosb +
sina sinb
tan(a + b) =
(tana +
tanb)/(1 -
tana
tanb)
provided a +
b
¹ ((2n + 1)p)/2
tan(a - b) =
(tana -
tanb)/(1 +
tana
tanb)
provided a -
b
¹ ((2n + 1)p)/2
Double angle formulae.
sin2a =
2sina cosa
cos2a =
cos2a -
sin2a
cos2a =
1 -
2sin2a
cos2a =
2cos2a -
1
tan2a =
(2tana)/(1 -
tan2a)
The sine rule.
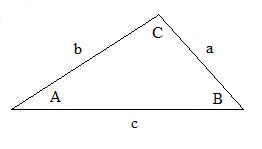
If a, b and c are the lengths of the sides in a triangle and A, B and C
are the sizes of the angles respectively opposite these sides then:
a/sinA =
b/sinB =
c/sinC
End of page.


