Colin James Physics - Physics data.

Last updated: 2nd April 2014.
Collision - elastic - one dimension - calculations and formulae.
Collision - elastic - two dimensions - example with calculations.
Electromagnetism - Fleming's Rules.
Electromagnetism - Maxwell's Equations.
Physical constants - recommended values.
SI prefixes and units.
Elastic collisions in 1 dimension.
Contents of this page.

1. Introduction.
2. Conservation of kinetic energy.
3. Conservation of linear momentum.
4. Formulae for u1 and u2.
5. General relationship: v1 - v2 = u2 - u1
6. Derivation (short) of formula for u1
7. Derivation (short) of formula for u2
8. Derivation (long) of formula for u1
9. Derivation (long) of formula for u2
10. Verify formulae for u1 and u2
1. Introduction.
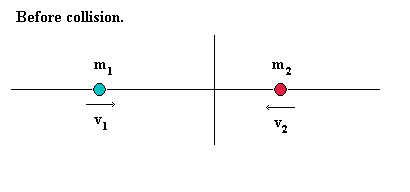
Two particles labelled 1 and 2 collide head on and rebound without loss of energy (elastic collision = kinetic energy is conserved).
Before they collide:
Particle 1 has mass m1 and speed v1
Particle 2 has mass m2 and speed v2
After they collide and rebound:
Particle 1 has mass m1 and speed u1
Particle 2 has mass m2 and speed u2
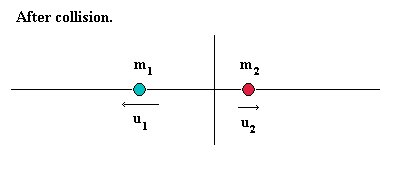
2. Kinetic energy conservation.
Kinetic energy conservation in a one dimensional elastic (kinetic energy conserving) collision requires that the total kinetic energy of both particles after the collision is the same as it was before the collision.
½m1v12 + ½m2v22 = ½m1u12 + ½m2u22 ----- (A)
3. Linear momentum conservation.
Linear momentum conservation in a one dimensional collision requires that the total linear momentum of both particles after the collision is the same as it was before the collision.
m1v1 + m2v2 = m1u1 + m2u2 ----- (B)
4. Formulae for u1 and u2.
Given m1, m2, v1 and v2 we can solve for u1 and u2.
We can use the two equations (A) and (B) to find the two unknowns u1 and u2 in terms of m1, m2, v1 and v2
I'll show you the solutions first in case that is all you want. How to derive the solutions follows in sections 6 and 7.
Formulae for u1 and u2.
Collision: u1 = (2m2v2 + (m1 - m2)v1)/(m1 + m2) ----- (C)
Collision: u2 = (2m1v1 + (m2 - m1)v2)/(m1 + m2) ----- (D)
No collision: u1 = v1 ----- (E)
No collision: u2 = v2 ----- (F)
Equations (A) and (B) give second solutions u1 = v1 and u2 = v2 which correspond to no collision. Particles 1 and 2 carry on after passing each other with the same speeds as they had initially.
5. General Relationship: v1 - v2 = u2 - u1
There is the following general relationship between the initial and final speeds of the particles involved in an elastic collision.
v1 - v2 = u2 - u1
It is derived as follows:
u2 - u1 = (2m1v1 + (m2 - m1)v2)/(m1 + m2) - (2m2v2 + (m1 - m2)v1)/(m1 + m2)
u2 - u1 = (2m1v1 + m2v2 - m1v2 - 2m2v2 - m1v1 + m2v1)/(m1 + m2)
u2 - u1 = (m1v1 - m1v2 - m2v2 + m2v1)/(m1 + m2)
u2 - u1 = ((m1 + m2)v1 - (m1 + m2)v2)/(m1 + m2)
u2 - u1 = (v1 - v2)
v1 - v2 = u2 - u1
Please note that if there is no collision then (using formulae (E) and (F) above):
v1 - v2 = u1 - u2
6. Derivation (short) of formula for u1
To find a formula for u1 we need to eliminate u2 from equations (A) and (B) above. Section 8 shows one way using solutions to quadratic equations but it is a bit long. This section takes a short cut.
u1 is derived as follows:
In (B) collect terms in m1 and m2.
m1v1 + m2v2 = m1u1 + m2u2 ----- (B)
m1(v1 - u1) + m2(v2 - u2) = 0
m2(v2 - u2) = -m1(v1 - u1) ----- (1)
In (A) collect terms in m1 and m2.
½m1v12 + ½m2v22 = ½m1u12 + ½m2u22 ----- (A)
m1(v12 - u12) + m2(v22 - u22) = 0
m1(v1 + u1)(v1 - u1) + m2(v2 + u2)(v2 - u2) = 0
m1(v1 + u1)(v1 - u1) + (v2 + u2)m2(v2 - u2) = 0 ----- (2)
Put the value of m2(v2 - u2) from (1) into (2).
m1(v1 + u1)(v1 - u1) + (v2 + u2)(-m1(v1 - u1)) = 0
m1(v1 + u1)(v1 - u1) - m1(v2 + u2)(v1 - u1) = 0
Cancel through by m1(v1 - u1)
(v1 + u1) - (v2 + u2) = 0
v1 + u1 - v2 - u2 = 0
u2 = v1 + u1 - v2
Put this value of u2 in (1)
m2(v2 - u2) = -m1(v1 - u1) ----- (1)
m2(v2 - (v1 + u1 - v2)) = -m1(v1 - u1)
m2(v2 - v1 - u1 + v2) = -m1(v1 - u1)
m2v2 - m2v1 - m2u1 + m2v2 = -m1v1 + m1u1
m2v2 - m2v1 + m2v2 = -m1v1 + u1(m1 + m2)
2m2v2 + m1v1 - m2v1 = u1(m1 + m2)
2m2v2 + (m1 - m2)v1 = u1(m1 + m2)
u1(m1 + m2) = 2m2v2 + (m1 - m2)v1
u1 = (2m2v2 + (m1 - m2)v1)/(m1 + m2)
The solution corresponding to a collision is:
u1 = (2m2v2 + (m1 - m2)v1)/(m1 + m2)
The solution:
u1 = v1 (and therefore u2 = v2)
corresponds to no collision and no change of particle speed.
7. Derivation (short) of formula for u2
To find a formula for u2 we need to eliminate u1 from equations (A) and (B) above. Section 8 shows one way using solutions to quadratic equations but it is a bit long. This section takes a short cut.
u2 is derived as follows:
In (B) collect terms in m1 and m2.
m1v1 + m2v2 = m1u1 + m2u2 ----- (B)
m1(v1 - u1) + m2(v2 - u2) = 0
m1(v1 - u1) = -m2(v2 - u2) ----- (1)
In (A) collect terms in m1 and m2.
½m1v12 + ½m2v22 = ½m1u12 + ½m2u22 ----- (A)
m1(v12 - u12) + m2(v22 - u22) = 0
m1(v1 + u1)(v1 - u1) + m2(v2 + u2)(v2 - u2) = 0
(v1 + u1)m1(v1 - u1) + m2(v2 + u2)(v2 - u2) = 0 ----- (2)
Put the value of m1(v1 - u1) from (1) into (2).
(v1 + u1)(-m2(v2 - u2)) + m2(v2 + u2)(v2 - u2) = 0
(-m2)(v1 + u1)(v2 - u2) + m2(v2 + u2)(v2 - u2) = 0
Cancel through by m2(v2 - u2)
-(v1 + u1) + (v2 + u2) = 0
-v1 - u1 + v2 + u2 = 0
-v1 + v2 + u2 = u1
u1 = -v1 + v2 + u2
Put this value of u1 in (1)
m1(v1 - u1) = -m2(v2 - u2) ----- (1)
m1(v1 - (-v1 + v2 + u2)) = -m2(v2 - u2)
m1(v1 + v1 - v2 - u2) = -m2(v2 - u2)
m1v1 + m1v1 - m1v2 - m1u2 = -m2v2 + m2u2
2m1v1 - m1v2 + m2v2 = m1u2 + m2u2
2m1v1 + (m2 - m1)v2 = u2(m1 + m2)
u2(m1 + m2) = 2m1v1 + (m2 - m1)v2
u2 = (2m1v1 + (m2 - m1)v2)/(m1 + m2)
The solution corresponding to a collision is:
u2 = (2m1v1 + (m2 - m1)v2)/(m1 + m2)
The solution:
u2 = v2 (and therefore u1 = v1)
corresponds to no collision and no change of particle speed.
8. Derivation (long) of formula for u1
This section is a bit long so I thought I would keep you interested by showing you a picture.

To find a formula for u1 we need to eliminate u2 from equations (A) and (B) above.
It is derived as follows:
From (B) find u2 in terms of u1.
m1v1 + m2v2 = m1u1 + m2u2 ----- (B)
m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2 - m1u1
u2 = (m1v1 + m2v2 - m1u1)/m2
Put the value of u2 in equation (A).
½m1v12 + ½m2v22 = ½m1u12 + ½m2u22 ----- (A)
m1v12 + m2v22 = m1u12 + m2u22
m1v12 + m2v22 = m1u12 + m2((m1v1 + m2v2 - m1u1)/m2)2
m1v12 + m2v22 = m1u12 + ((m1v1 + m2v2 - m1u1)2)/m2
m1m2v12 + m22v22 = m1m2u12 + (m1v1 + m2v2 - m1u1)2
To expand the inside of the (parentheses (brackets))2 [that is: (m1v1 + m2v2 - m1u1)2] you may see what is going on more clearly with this example:
(a + b - c)2 =
(a + b - c)(a + b - c) =
a2 + ab - ac + ba + b2 - bc - ca - cb + c2
a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab - 2ac - 2bc
m1m2v12 + m22v22 = m1m2u12 + (m12v12 + m22v22 + m12u12 + 2m1m2v1v2 - 2m1m1v1u1 - 2m1m2v2u1)
Removing m22v22 from both sides:
m1m2v12 = m1m2u12 + m12v12 + m12u12 + 2m1m2v1v2 - 2m1m1v1u1 - 2m1m2v2u1
Dividing through by m1:
m2v12 = m2u12 + m1v12 + m1u12 + 2m2v1v2 - 2m1v1u1 - 2m2v2u1
Turning the equation the other way round and collecting terms in u1:
m1u12+ m2u12 - 2m1v1u1 - 2m2v2u1 + m1v12- m2v12 + 2m2v1v2 = 0
(m1 + m2)u12 - 2(m1v1 + m2v2)u1 + (m1 - m2)v12 + 2m2v1v2 = 0
Quadratic in u1
We now have a quadratic equation in u1 so we can put the values into the standard solution: x = (-b ±Ö(b2 - 4ac))/2a
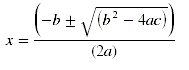
of the quadratic equation: ax2 + bx + c = 0
Substituting u1 for x we get: u1 = (-b ±Ö(b2 - 4ac))/2a
which are the solutions of the quadratic equation: au12 + bu1 + c = 0
Where:
a = (m1 + m2)
b = - 2(m1v1 + m2v2)
c = ((m1 - m2)v12 + 2m2v1v2)
The part under the square root sign (b2 - 4ac) can be simplified before filling out the whole formula:
(b2 - 4ac) = (- 2(m1v1 + m2v2))2 - 4(m1 + m2)((m1 - m2)v12 + 2m2v1v2)
(b2 - 4ac) = 4(m12v12 + 2m1m2v1v2 + m22v22) - 4(m12v12 - m1m2v12 + 2m1m2v1v2 + m1m2v12 - m22v12 + 2m22v1v2)
(b2 - 4ac) = 4(m12v12 + 2m1m2v1v2 + m22v22- m12v12 + m1m2v12 - 2m1m2v1v2 - m1m2v12 + m22v12 - 2m22v1v2)
(b2 - 4ac) = 4((m12v12 - m12v12) + (2m1m2v1v2 - 2m1m2v1v2) + m22v22 + (m1m2v12 - m1m2v12) + m22v12 - 2m22v1v2)
(b2 - 4ac) = 4(m22v22 + m22v12 - 2m22v1v2)
(b2 - 4ac) = 4m22(v22 + v12 - 2v1v2)
(b2 - 4ac) = 4m22(v12 - 2v1v2+ v22)
(b2 - 4ac) = 4m22(v1 - v2)2
Time for another picture.

Back to filling in the solution for the quadratic equation in u1: u1 = (-b ±Ö(b2 - 4ac))/2a
u1 = (-(- 2(m1v1 + m2v2)) ±Ö(4m22(v1 - v2)2))/2(m1 + m2)
u1 = (2(m1v1 + m2v2) ± (2m2(v1 - v2)))/2(m1 + m2)
u1 = (m1v1 + m2v2 ± m2(v1 - v2))/(m1 + m2)
u1 = (m1v1 + m2v2 + m2(v1 - v2))/(m1 + m2)
or u1 = (m1v1 + m2v2 - m2(v1 - v2))/(m1 + m2)
u1 = (m1v1 + m2v2 + m2v1 - m2v2)/(m1 + m2)
or u1 = (m1v1 + m2v2 - m2v1 + m2v2)/(m1 + m2)
u1 = ((m1 + m2)v1)/(m1 + m2)
or u1 = (2m2v2 + (m1 - m2)v1)/(m1 + m2)
u1 = v1
or u1 = (2m2v2 + (m1 - m2)v1)/(m1 + m2)
The solution corresponding to a collision is:
u1 = (2m2v2 + (m1 - m2)v1)/(m1 + m2)
The solution:
u1 = v1
corresponds to no collision and no change of particle speed.
9. Derivation (long) of formula for u2
Because of the symmetry (in the mathematics) of the kinetic energy (A) and linear momentum (B) equations we can deduce the formula for u2 from that of u1 by interchanging the subscripts 1 and 2 as follows:
u1 = (2m2v2 + (m1 - m2)v1)/(m1 + m2)
u2 = (2m1v1 + (m2 - m1)v2)/(m2 + m1) = (2m1v1 + (m2 - m1)v2)/(m1 + m2)

I also show the full deduction here:
To find a formula for u2 we need to eliminate u1 from equations (A) and (B) above.
It is derived as follows:
From (B) find u1 in terms of u2.
m2v2 + m1v1 = m2u2 + m1u1 ----- (B)
m1u1 = m2v2 + m1v1 - m2u2
u1 = (m2v2 + m1v1 - m2u2)/m1
Put the value of u1 in equation (A).
½m2v22 + ½m1v12 = ½m2u22 + ½m1u12 ----- (A)
m2v22 + m1v12 = m2u22 + m1u12
m2v22 + m1v12 = m2u22 + m1((m2v2 + m1v1 - m2u2)/m1)2
m2v22 + m1v12 = m2u22 + ((m2v2 + m1v1 - m2u2)2)/m1
m2m1v22 + m12v12 = m2m1u22 + (m2v2 + m1v1 - m2u2)2
To expand the inside of the (parentheses (brackets))2 [that is: (m2v2 + m1v1 - m2u2)2] you may see what is going on more clearly with this example:
(a + b - c)2 =
(a + b - c)(a + b - c) =
a2 + ab - ac + ba + b2 - bc - ca - cb + c2
a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab - 2ac - 2bc
m2m1v22 + m12v12 = m2m1u22 + (m22v22 + m12v12 + m22u22 + 2m2m1v2v1 - 2m2m2v2u2 - 2m2m1v1u2)
Removing m12v12 from both sides:
m2m1v22 = m2m1u22 + m22v22 + m22u22 + 2m2m1v2v1 - 2m2m2v2u2 - 2m2m1v1u2
Dividing through by m2:
m1v22 = m1u22 + m2v22 + m2u22 + 2m1v2v1 - 2m2v2u2 - 2m1v1u2
Turning the equation the other way round and collecting terms in u2:
m2u22+ m1u22 - 2m2v2u2 - 2m1v1u2 + m2v22- m1v22 + 2m1v2v1 = 0
(m2 + m1)u22 - 2(m2v2 + m1v1)u2 + (m2 - m1)v22 + 2m1v2v1 = 0
Quadratic in u2
We now have a quadratic equation in u2 so we can put the values into the standard solution: x = (-b ±Ö(b2 - 4ac))/2a
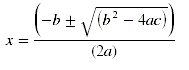
of the quadratic equation: ax2 + bx + c = 0
Substituting u2 for x we get: u2 = (-b ±Ö(b2 - 4ac))/2a
which are the solutions of the quadratic equation: au22 + bu2 + c = 0
Where:
a = (m2 + m1)
b = - 2(m2v2 + m1v1)
c = ((m2 - m1)v22 + 2m1v2v1)
The part under the square root sign (b2 - 4ac) can be simplified before filling out the whole formula:
(b2 - 4ac) = (- 2(m2v2 + m1v1))2 - 4(m2 + m1)((m2 - m1)v22 + 2m1v2v1)
(b2 - 4ac) = 4(m22v22 + 2m2m1v2v1 + m12v12) - 4(m22v22 - m2m1v22 + 2m2m1v2v1 + m2m1v22 - m12v22 + 2m12v2v1)
(b2 - 4ac) = 4(m22v22 + 2m2m1v2v1 + m12v12- m22v22 + m2m1v22 - 2m2m1v2v1 - m2m1v22 + m12v22 - 2m12v2v1)
(b2 - 4ac) = 4((m22v22 - m22v22) + (2m2m1v2v1 - 2m2m1v2v1) + m12v12 + (m2m1v22 - m2m1v22) + m12v22 - 2m12v2v1)
(b2 - 4ac) = 4(m12v12 + m12v22 - 2m12v2v1)
(b2 - 4ac) = 4m12(v12 + v22 - 2v2v1)
(b2 - 4ac) = 4m12(v22 - 2v2v1+ v12)
(b2 - 4ac) = 4m12(v2 - v1)2
Time for another picture.

Back to filling in the solution for the quadratic equation in u2: u2 = (-b ±Ö(b2 - 4ac))/2a
u2 = (-(- 2(m2v2 + m1v1)) ±Ö(4m12(v2 - v1)2))/2(m2 + m1)
u2 = (2(m2v2 + m1v1) ± (2m1(v2 - v1)))/2(m2 + m1)
u2 = (m2v2 + m1v1 ± m1(v2 - v1))/(m2 + m1)
u2 = (m2v2 + m1v1 + m1(v2 - v1))/(m2 + m1)
or u2 = (m2v2 + m1v1 - m1(v2 - v1))/(m2 + m1)
u2 = (m2v2 + m1v1 + m1v2 - m1v1)/(m2 + m1)
or u2 = (m2v2 + m1v1 - m1v2 + m1v1)/(m2 + m1)
u2 = ((m2 + m1)v2)/(m2 + m1)
or u2 = (2m1v1 + (m2 - m1)v2)/(m2 + m1)
u2 = v2
or u2 = (2m1v1 + (m2 - m1)v2)/(m2 + m1)
The solution corresponding to a collision is:
u2 = (2m1v1 + (m2 - m1)v2)/(m2 + m1)
The solution:
u2 = v2
corresponds to no collision and no change of particle speed.
10. Verify formulae for u1 and u2
We need to check that the formulae for u1:
u1 = (2m2v2 + (m1 - m2)v1)/(m1 + m2) ----- (C)
and u2:
u2 = (2m1v1 + (m2 - m1)v2)/(m1 + m2) ----- (D)
solve the kinetic energy equation:
½m1v12 + ½m2v22 = ½m1u12 + ½m2u22 ----- (A)
and the linear momentum equation:
m1v1 + m2v2 = m1u1 + m2u2 ----- (B)
by substituting them into the right hand sides of the equations and making sure both sides of the equations are equal.
Verifying the kinetic energy equation.
½m1u12 + ½m2u22
= ½m1((2m2v2 + (m1 - m2)v1)/(m1 + m2))2 + ½m2((2m1v1 + (m2 - m1)v2)/(m1 + m2))2
= {½/(m1 + m2)2}{m1(2m2v2 + (m1 - m2)v1)2 + m2(2m1v1 + (m2 - m1)v2)2}
= {½/(m1 + m2)2}{m1(4m22v22 + 4m2v2(m1 - m2)v1 + (m1 - m2)2v12) + m2(4m12v12 + 4m1v1(m2 - m1)v2 + (m2 - m1)2v22)}
= {½/(m1 + m2)2}{m1(4m22v22 + 4m1m2v1v2 - 4m22v1v2 + m12v12 - 2m1m2v12 + m22v12)
+ m2(4m12v12 + 4m1m2v1v2 - 4m12v1v2 + m22v22 - 2m1m2v22 + m12v22}
I have put in bold terms that cancel out:
= {½/(m1 + m2)2}{4m1m22v22 + 4m12m2v1v2 - 4m1m22v1v2 + m13v12 - 2m12m2v12 + m1m22v12
+ 4m12m2v12 + 4m1m22v1v2 - 4m12m2v1v2 + m23v22 - 2m1m22v22 + m12m2v22}
= {½/(m1 + m2)2}{4m1m22v22 + m13v12 - 2m12m2v12 + m1m22v12
+ 4m12m2v12 + m23v22 - 2m1m22v22 + m12m2v22}
= {½/(m1 + m2)2}{2m1m22v22 + m13v12 + m1m22v12
+ 2m12m2v12 + m23v22 + m12m2v22}
= {½/(m1 + m2)2}{m13v12
+ 2m12m2v12 + m1m22v12 + m12m2v22 + 2m1m22v22 + m23v22}
= {½/(m1 + m2)2}{[m12
+ 2m1m2 + m22]m1v12 + [m12 + 2m1m2 + m22]m2v22}
= {½/(m1 + m2)2}{[(m1 + m2)2]m1v12 + [(m1 + m2)2]m2v22}
= {½}{m1v12 + m2v22}
= ½m1v12 + ½m2v22 ----- Q.E.D. {The right hand side of the kinetic energy equation equals the left hand side.}
Verifying the linear momentum equation.
m1u1 + m2u2
= m1(2m2v2 + (m1 - m2)v1)/(m1 + m2) + m2(2m1v1 + (m2 - m1)v2)/(m1 + m2)
= [m1(2m2v2 + (m1 - m2)v1) + m2(2m1v1 + (m2 - m1)v2)]/(m1 + m2)
= [2m1m2v2 + m12v1 - m1m2v1 + 2m1m2v1 + m22v2 - m1m2v2]/(m1 + m2)
= [m1m2v2 + m12v1 + m1m2v1 + m22v2]/(m1 + m2)
= [m12v1 + m1m2v1 + m1m2v2 + m22v2]/(m1 + m2)
= [(m1 + m2)m1v1 + (m1 + m2)m2v2]/(m1 + m2)
= m1v1 + m2v2 ----- Q.E.D. {The right hand side of the linear momentum equation equals the left hand side.}
End of page.


